Antibody Drug Conjugates
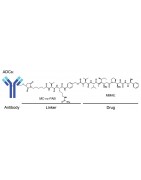
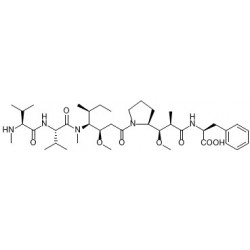
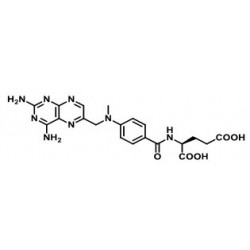
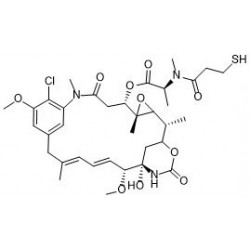
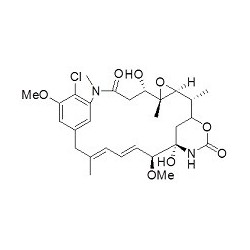
Antibody-drug conjugates or ADCs are a new class of highly potent biopharmaceutical drugs designed as a targeted therapy for the treatment of people with cancer. ADCs are complex molecules composed of an antibody (a whole mAb or an antibody fragment such as a single-chain variable fragment [scFv]) linked, via a stable, chemical, linker with labile bonds, to a biological active cytotoxic (anticancer) payload or drug. Antibody Drug Conjugates are examples of bioconjugates and immunoconjugates.
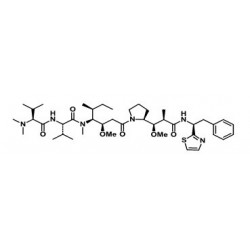
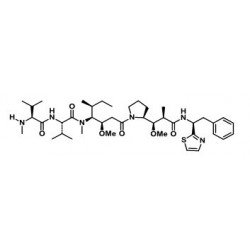
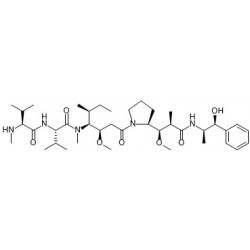
- Drugs: MMAE, MMAF, DM1, DM4 and etc.
- Linkers: MC-Val-Cit-PAB-PNP, Fmoc-VC-PAB-PNP, SMCC, MMC and etc.
- Drug-linkers:DM1-SMCC, MC-Val-Cit-PAB-MMAE, MC-Val-Cit-PAB-MMAF, SuO-Val-Cit--PAB-MMAE and etc.